
You are viewing documentation for KubeSphere version:v3.0.0
KubeSphere v3.0.0 documentation is no longer actively maintained. The version you are currently viewing is a static snapshot. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Auditing Log Query
KubeSphere supports the query of auditing logs among isolated tenants. This tutorial demonstrates how to use the query function, including the interface, search parameters and detail pages.
Prerequisites
You need to enable KubeSphere Auditing Logs.
Enter the Query Interface
-
The query function is available for all users. Log in to the console with any account, hover over the Toolbox in the lower right corner and select Auditing Operating.
Note
Any account has the authorization to query auditing logs, while the logs each account is able to see are different.
- If an account has the authorization of viewing resources in a project, it can see the auditing log that happens in this project, such as workload creation in the project.
- If an account has the authorization of listing projects in a workspace, it can see the auditing log that happens in this workspace but not in projects, such as project creation in the workspace.
- If an account has the authorization of listing projects in a cluster, it can see the auditing log that happens in this cluster but not in workspaces and projects, such as workspace creation in the cluster.
-
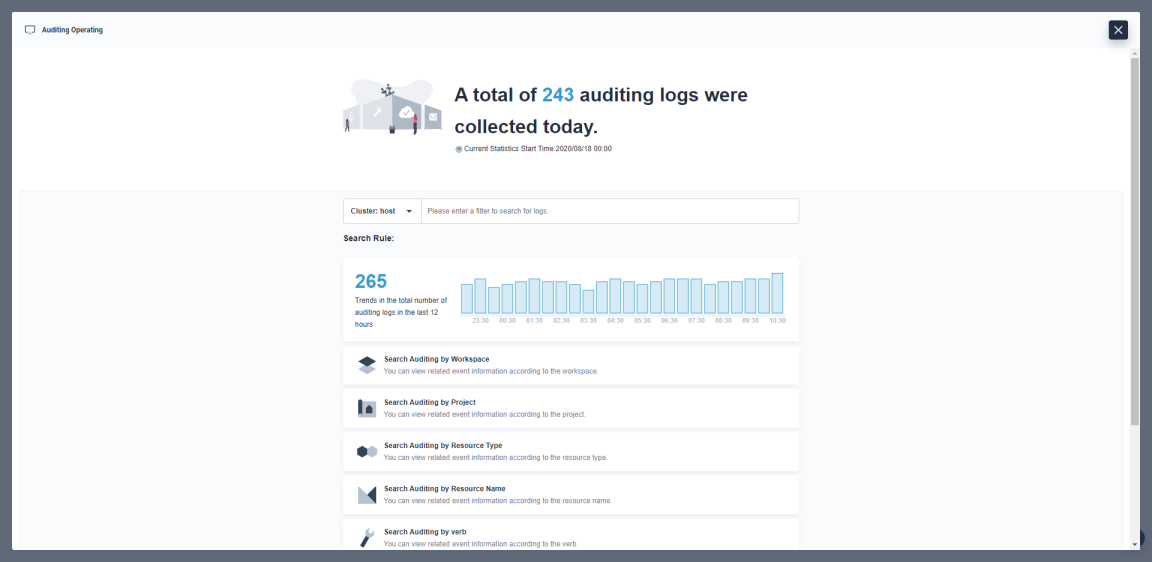
As shown in the pop-up window, you can see trends in the total number of auditing logs in the last 12 hours.
-
The Auditing Operating console supports the following query parameters:
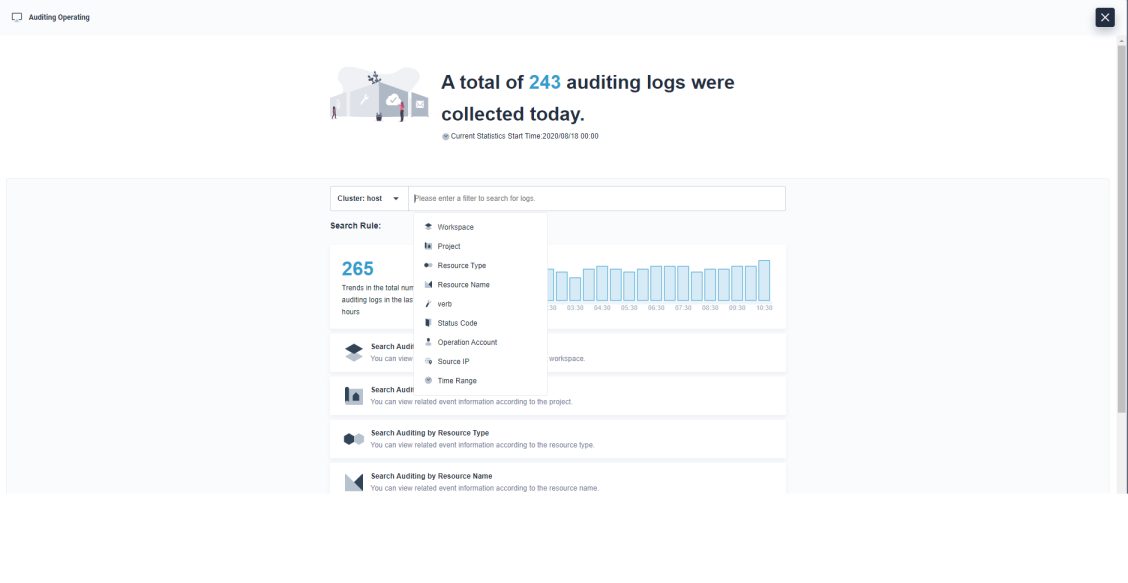
Parameter Description Cluster The cluster where the operation happens. It is enabled if the multi-cluster feature is turned on. Project The project where the operation happens. It supports exact query and fuzzy query. Workspace The workspace where the operation happens. It supports exact query and fuzzy query. Resource Type The type of resource associated with the request. It supports fuzzy query. Resource Name The name of the resource associated with the request. It supports fuzzy query. Verb The Kubernetes verb associated with the request. For non-resource requests, this is the lower-case HTTP method. It supports exact query. Status Code The Http response code. It supports exact query. Operation Account The user who calls this request. It supports exact and fuzzy query. Source IP The IP address from where the request originated and intermediate proxies. It supports fuzzy query. Time Range The time when the request reaches the apiserver. Note
- Fuzzy query supports case-insensitive fuzzy matching and retrieval of full terms by the first half of a word or phrase based on Elasticsearch segmentation rules.
- KubeSphere stores logs for the last seven days by default. You can modify the retention period in the ConfigMap
elasticsearch-logging-curator.
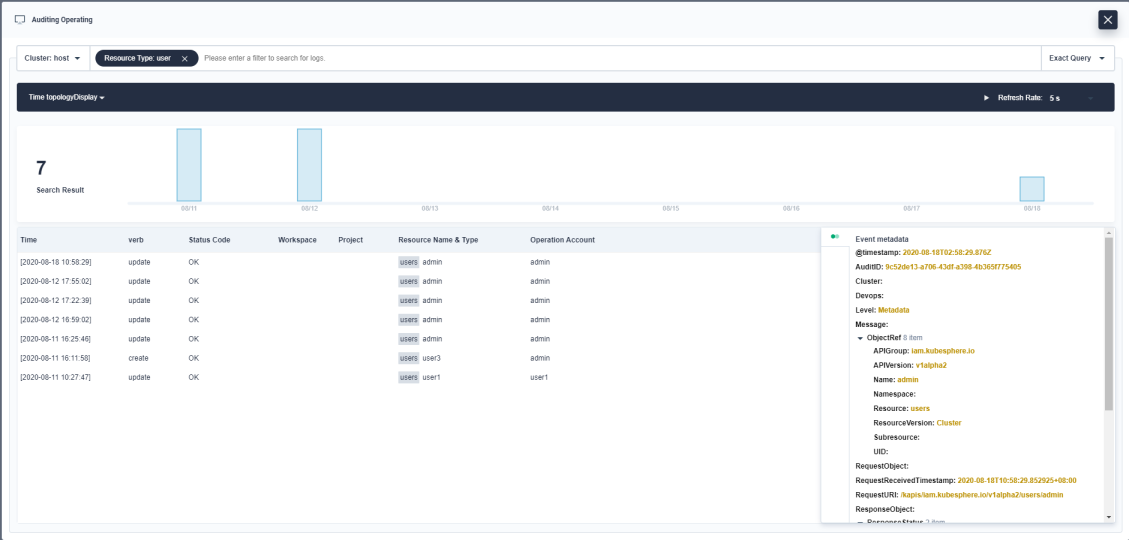
Enter Query Parameters
-
Select a filter and input the keyword you want to search. For example, query auditing logs containing the information of
userchanged as shown in the following screenshot: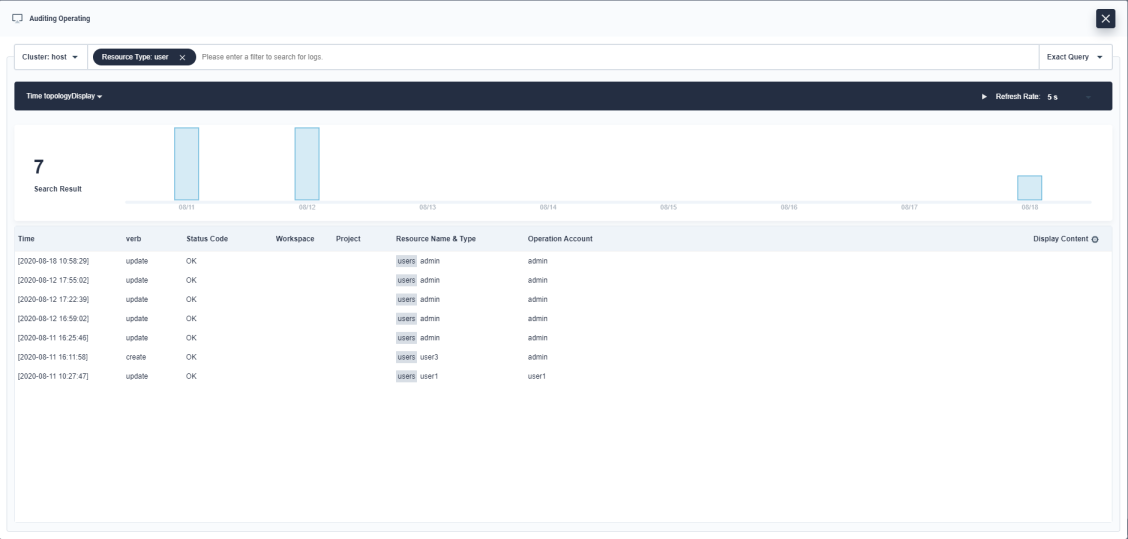
-
Click any one of the results from the list, and you can see the detail of the auditing log.













 Previous
Previous
