
You are viewing documentation for KubeSphere version:v3.0.0
KubeSphere v3.0.0 documentation is no longer actively maintained. The version you are currently viewing is a static snapshot. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Agent Connection
The component Tower of KubeSphere is used for agent connection. Tower is a tool for network connection between clusters through the agent. If the Host Cluster (H Cluster) cannot access the Member Cluster (M Cluster) directly, you can expose the proxy service address of the H cluster. This enables the M Cluster to connect to the H Cluster through the agent. This method is applicable when the M Cluster is in a private environment (for example, IDC) and the H Cluster is able to expose the proxy service. The agent connection is also applicable when your clusters are distributed across different cloud providers.
To use the multi-cluster feature using an agent, you must have at least two clusters serving as the H Cluster and the M Cluster respectively. A cluster can be defined as the H Cluster or the M Cluster either before or after you install KubeSphere. For more information about installing KubeSphere, refer to Installing on Linux and Installing on Kubernetes.
Video Demonstration
Prepare a Host Cluster
A host cluster provides you with the central control plane and you can only define one host cluster.
If you already have a standalone KubeSphere cluster installed, you can set the value of clusterRole to host by editing the cluster configuration.
-
Option A - Use the web console:
Use the
adminaccount to log in to the console and go to CRDs on the Cluster Management page. Enter the keywordClusterConfigurationand go to its detail page. Edit the YAML ofks-installer, which is similar to Enable Pluggable Components. -
Option B - Use Kubectl:
kubectl edit cc ks-installer -n kubesphere-system
In the YAML file of ks-installer, navigate to multicluster, set the value of clusterRole to host, then click Update (if you use the web console) to make it effective:
multicluster:
clusterRole: host
You need to wait for a while so that the change can take effect.
You can define a host cluster before you install KubeSphere either on Linux or on an existing Kubernetes cluster. If you want to install KubeSphere on Linux, you use a config-sample.yaml file. If you want to install KubeSphere on an existing Kubernetes cluster, you use two YAML files, one of which is cluster-configuration.yaml. To set a host cluster, change the value of clusterRole to host in config-sample.yaml or cluster-configuration.yaml accordingly before you install KubeSphere.
multicluster:
clusterRole: host
Note
config-sample.yaml file. In this case, you can set a host cluster after KubeSphere is installed.You can use kubectl to retrieve the installation logs to verify the status by running the following command. Wait for a while, and you will be able to see the successful log return if the host cluster is ready.
kubectl logs -n kubesphere-system $(kubectl get pod -n kubesphere-system -l app=ks-install -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -f
Set the Proxy Service Address
After the installation of the host cluster, a proxy service called tower will be created in kubesphere-system, whose type is LoadBalancer.
If a LoadBalancer plugin is available for the cluster, you can see a corresponding address for EXTERNAL-IP of tower, which will be acquired by KubeSphere. In this case, the proxy service is set automatically. That means you can skip the step to set the proxy. Execute the following command to verify if you have a LoadBalancer.
kubectl -n kubesphere-system get svc
The output is similar to this:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
tower LoadBalancer 10.233.63.191 139.198.110.23 8080:30721/TCP 16h
Note
-
If you cannot see a corresponding address displayed (
EXTERNAL-IPispending), you need to manually set the proxy address. For example, you have an available public IP address139.198.120.120, and port8080of this IP address has been forwarded to port30721of the cluster. Execute the following command to check the service.kubectl -n kubesphere-system get svcThe output is similar to this:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE tower LoadBalancer 10.233.63.191 <pending> 8080:30721/TCP 16h -
Add the value of
proxyPublishAddressto the configuration file ofks-installerand input the public IP address (139.198.120.120in this tutorial) and port number as follows.-
Option A - Use the web console:
Use the
adminaccount to log in to the console and go to CRDs on the Cluster Management page. Enter the keywordClusterConfigurationand go to its detail page. Edit the YAML ofks-installer, which is similar to Enable Pluggable Components. -
Option B - Use Kubectl:
kubectl -n kubesphere-system edit clusterconfiguration ks-installer
Navigate to
multiclusterand add a new line forproxyPublishAddressto define the IP address to access tower.multicluster: clusterRole: host proxyPublishAddress: http://139.198.120.120:8080 # Add this line to set the address to access tower -
-
Save the configuration and wait for a while, or you can manually restart
ks-apiserverto make the change effective immediately using the following command.kubectl -n kubesphere-system rollout restart deployment ks-apiserver
Prepare a Member Cluster
In order to manage the member cluster from the host cluster, you need to make jwtSecret the same between them. Therefore, get it first by excuting the following command on the host cluster.
kubectl -n kubesphere-system get cm kubesphere-config -o yaml | grep -v "apiVersion" | grep jwtSecret
The output may look like this:
jwtSecret: "gfIwilcc0WjNGKJ5DLeksf2JKfcLgTZU"
If you already have a standalone KubeSphere cluster installed, you can set the value of clusterRole to member by editing the cluster configuration.
-
Option A - Use the web console:
Use the
adminaccount to log in to the console and go to CRDs on the Cluster Management page. Enter the keywordClusterConfigurationand go to its detail page. Edit the YAML ofks-installer, which is similar to Enable Pluggable Components. -
Option B - Use Kubectl:
kubectl edit cc ks-installer -n kubesphere-system
In the YAML file of ks-installer, input the corresponding jwtSecret shown above:
authentication:
jwtSecret: gfIwilcc0WjNGKJ5DLeksf2JKfcLgTZU
Scroll down and set the value of clusterRole to member, then click Update (if you use the web console) to make it effective:
multicluster:
clusterRole: member
You need to wait for a while so that the change can take effect.
You can define a member cluster before you install KubeSphere either on Linux or on an existing Kubernetes cluster. If you want to install KubeSphere on Linux, you use a config-sample.yaml file. If you want to install KubeSphere on an existing Kubernetes cluster, you use two YAML files, one of which is cluster-configuration.yaml. To set a member cluster, input the value of jwtSecret shown above and change the value of clusterRole to member in config-sample.yaml or cluster-configuration.yaml accordingly before you install KubeSphere.
authentication:
jwtSecret: gfIwilcc0WjNGKJ5DLeksf2JKfcLgTZU
multicluster:
clusterRole: member
Note
config-sample.yaml file. In this case, you can set a member cluster after KubeSphere is installed.You can use kubectl to retrieve the installation logs to verify the status by running the following command. Wait for a while, and you will be able to see the successful log return if the member cluster is ready.
kubectl logs -n kubesphere-system $(kubectl get pod -n kubesphere-system -l app=ks-install -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -f
Import a Member Cluster
-
Log in to the KubeSphere console as
adminand click Add Cluster on the Clusters Management page.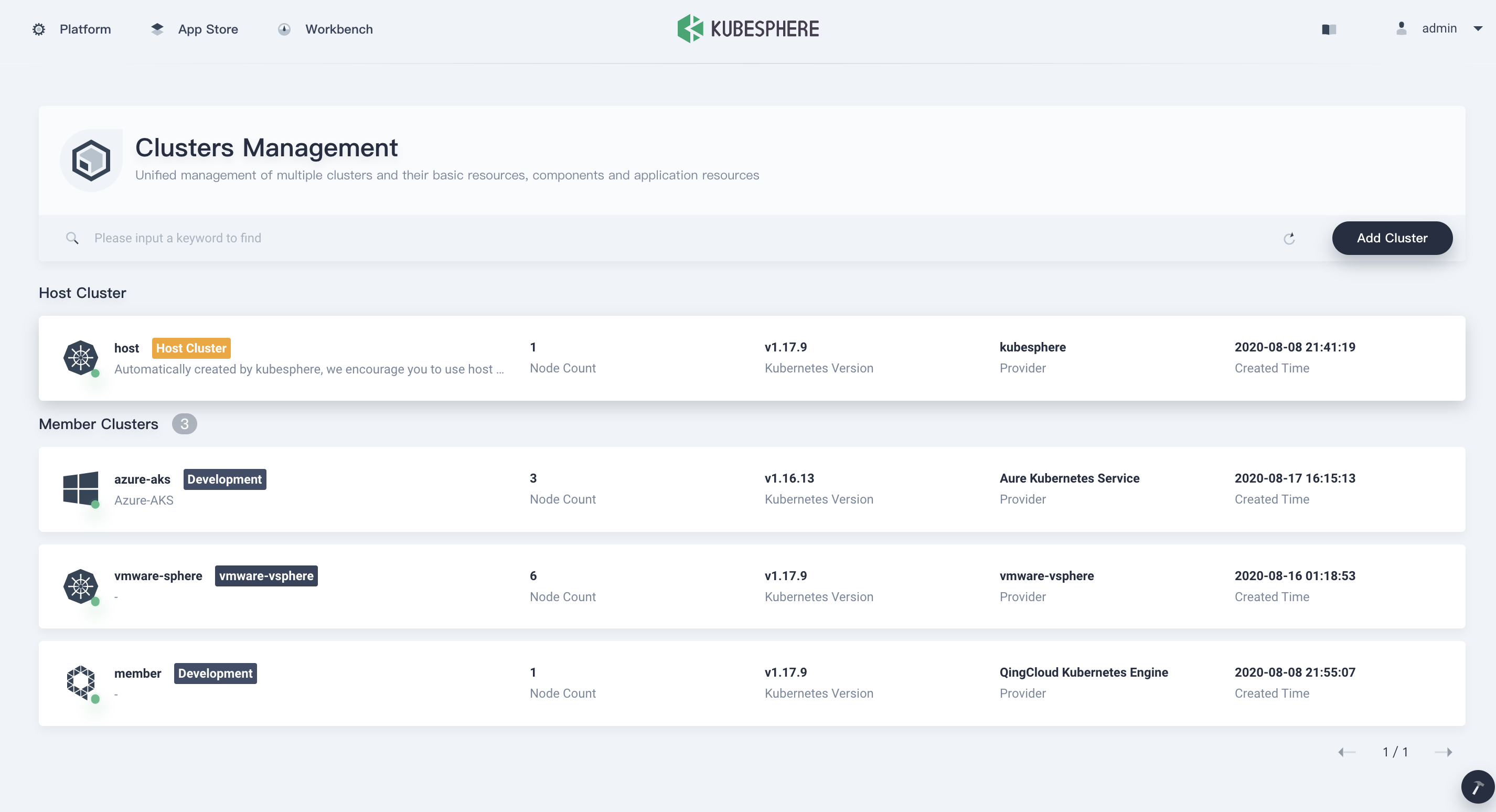
-
Enter the basic information of the cluster to be imported and click Next.
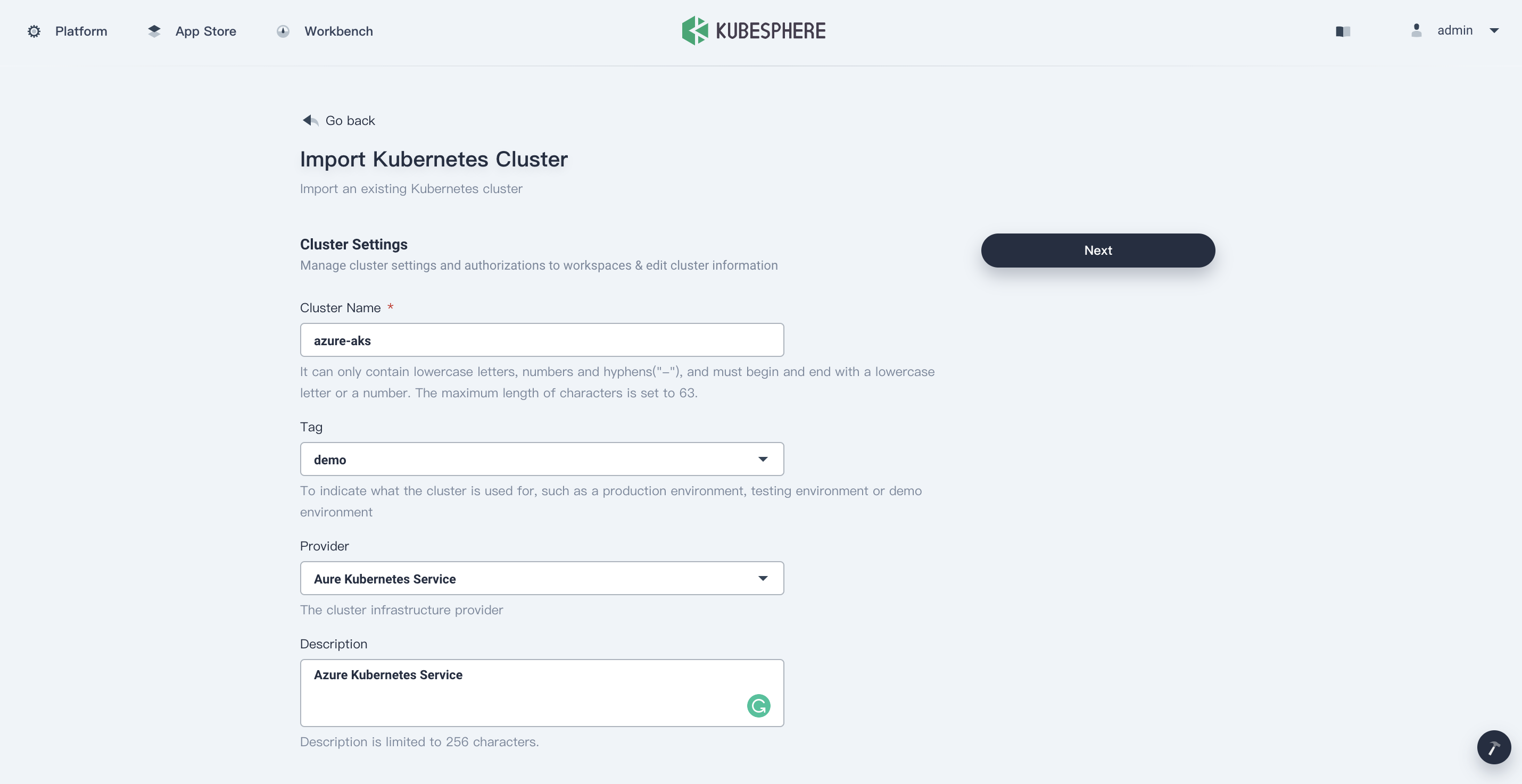
-
In Connection Method, select Cluster connection agent and click Import. It will show the agent deployment generated by the H Cluster in the console.
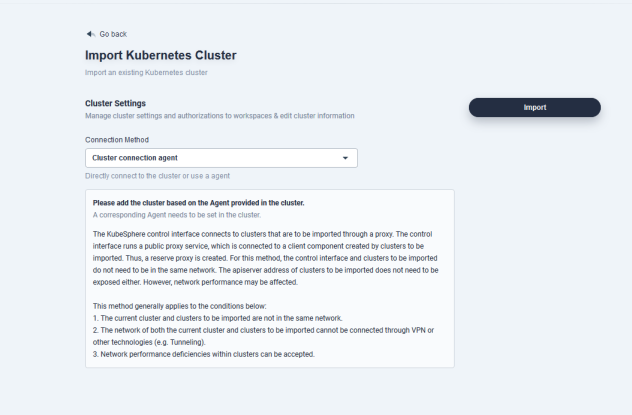
-
Create an
agent.yamlfile on the M Cluster based on the instruction, then copy and paste the agent deployment to the file. Executekubectl create -f agent.yamlon the node and wait for the agent to be up and running. Please make sure the proxy address is accessible to the M Cluster. -
You can see the cluster you have imported in the H Cluster when the cluster agent is up and running.
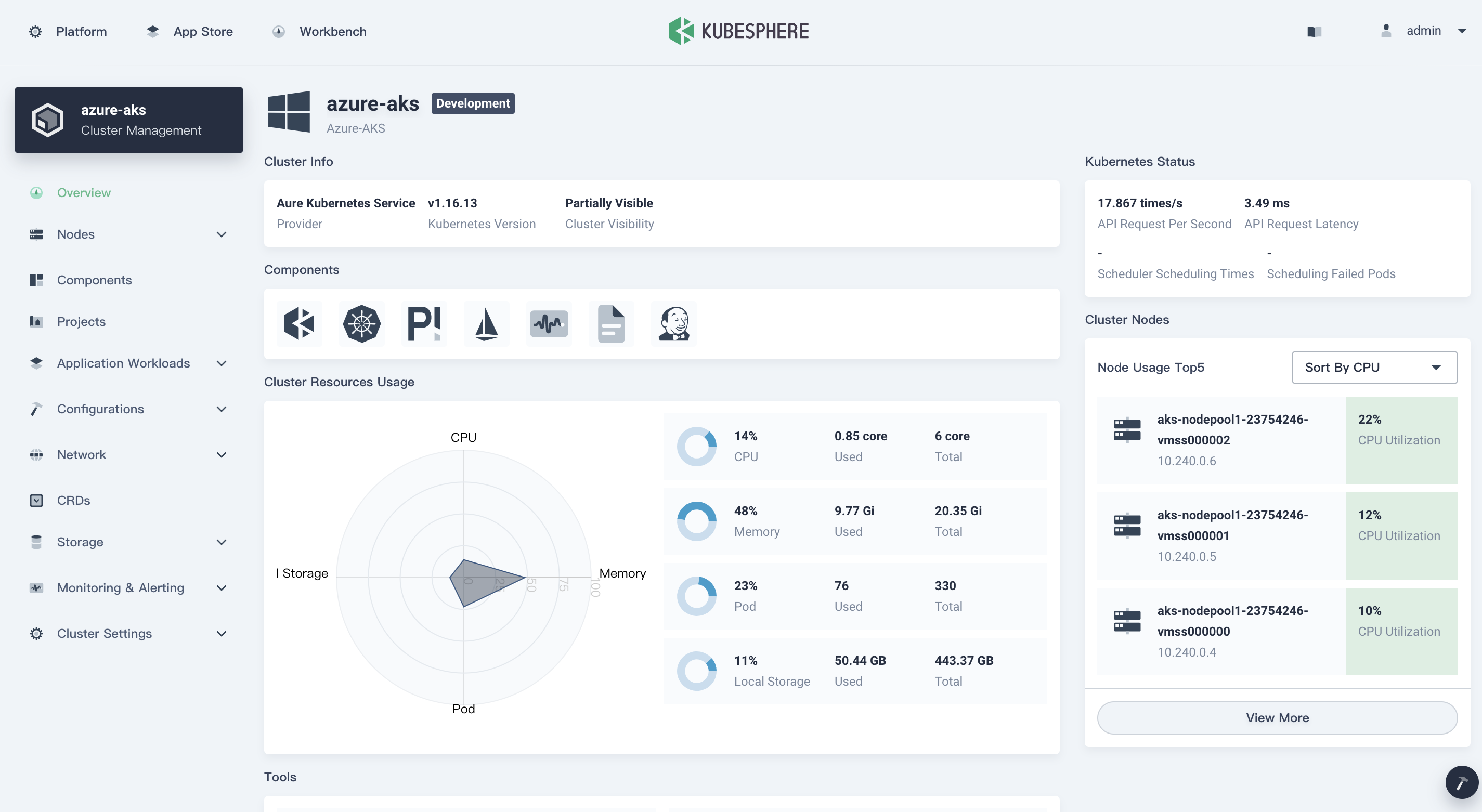













 Previous
Previous
