
You are viewing documentation for KubeSphere version:v3.0.0
KubeSphere v3.0.0 documentation is no longer actively maintained. The version you are currently viewing is a static snapshot. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
KubeSphere DevOps System
What is KubeSphere DevOps System
The KubeSphere DevOps System is designed for CI/CD workflows in Kubernetes. Based on Jenkins, it provides one-stop solutions to help both development and Ops teams build, test and publish apps to Kubernetes in a straight-forward way. It also features plugin management, Binary-to-Image (B2I), Source-to-Image (S2I), code dependency caching, code quality analysis, pipeline logging, etc.
The DevOps System offers an enabling environment for users as apps can be automatically released to the same platform. It is also compatible with third-party private image registries (for example, Harbor) and code repositories (for example, GitLab/GitHub/SVN/BitBucket). As such, it creates excellent user experiences by providing users with comprehensive, visualized CI/CD pipelines which are extremely useful in air-gapped environments.
For more information, see DevOps User Guide.
Enable DevOps before Installation
Installing on Linux
When you implement multi-node installation of KubeSphere on Linux, you need to create a configuration file, which lists all KubeSphere components.
-
In the tutorial of Installing KubeSphere on Linux, you create a default file
config-sample.yaml. Modify the file by executing the following command:vi config-sample.yamlNote
If you adopt All-in-One Installation, you do not need to create aconfig-sample.yamlfile as you can create a cluster directly. Generally, the all-in-one mode is for users who are new to KubeSphere and look to get familiar with the system. If you want to enable DevOps in this mode (for example, for testing purposes), refer to the following section to see how DevOps can be installed after installation. -
In this file, navigate to
devopsand changefalsetotrueforenabled. Save the file after you finish.devops: enabled: true # Change "false" to "true" -
Create a cluster using the configuration file:
./kk create cluster -f config-sample.yaml
Installing on Kubernetes
The process of installing KubeSphere on Kubernetes is same as stated in the tutorial of Installing KubeSphere on Kubernetes except the optional component DevOps needs to be enabled first in the cluster-configuration.yaml file.
-
Download the file cluster-configuration.yaml and open it for editing.
vi cluster-configuration.yaml -
In this local
cluster-configuration.yamlfile, navigate todevopsand enable DevOps by changingfalsetotrueforenabled. Save the file after you finish.devops: enabled: true # Change "false" to "true" -
Execute the following commands to start installation:
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubesphere/ks-installer/releases/download/v3.0.0/kubesphere-installer.yaml kubectl apply -f cluster-configuration.yaml
Enable DevOps after Installation
-
Log in to the console as
admin. Click Platform in the top-left corner and select Clusters Management.
-
Click CRDs and enter
clusterconfigurationin the search bar. Click the result to view its detail page.Info
A Custom Resource Definition (CRD) allows users to create a new type of resources without adding another API server. They can use these resources like any other native Kubernetes objects. -
In Resource List, click the three dots on the right of
ks-installerand select Edit YAML.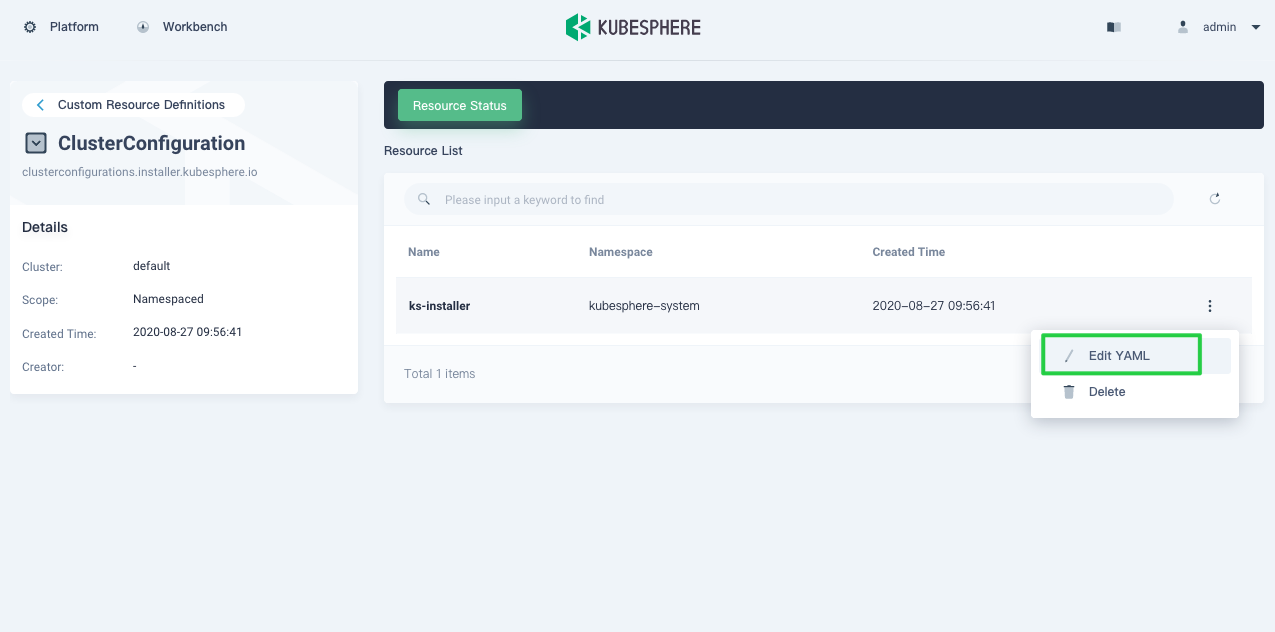
-
In this yaml file, navigate to
devopsand changefalsetotrueforenabled. After you finish, click Update in the bottom-right corner to save the configuration.devops: enabled: true # Change "false" to "true" -
You can use the web kubectl to check the installation process by executing the following command:
kubectl logs -n kubesphere-system $(kubectl get pod -n kubesphere-system -l app=ks-install -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}') -fTip
You can find the web kubectl tool by clicking the hammer icon in the bottom-right corner of the console.
Verify the Installation of the Component
Go to Components and check the status of DevOps. You may see an image as follows:
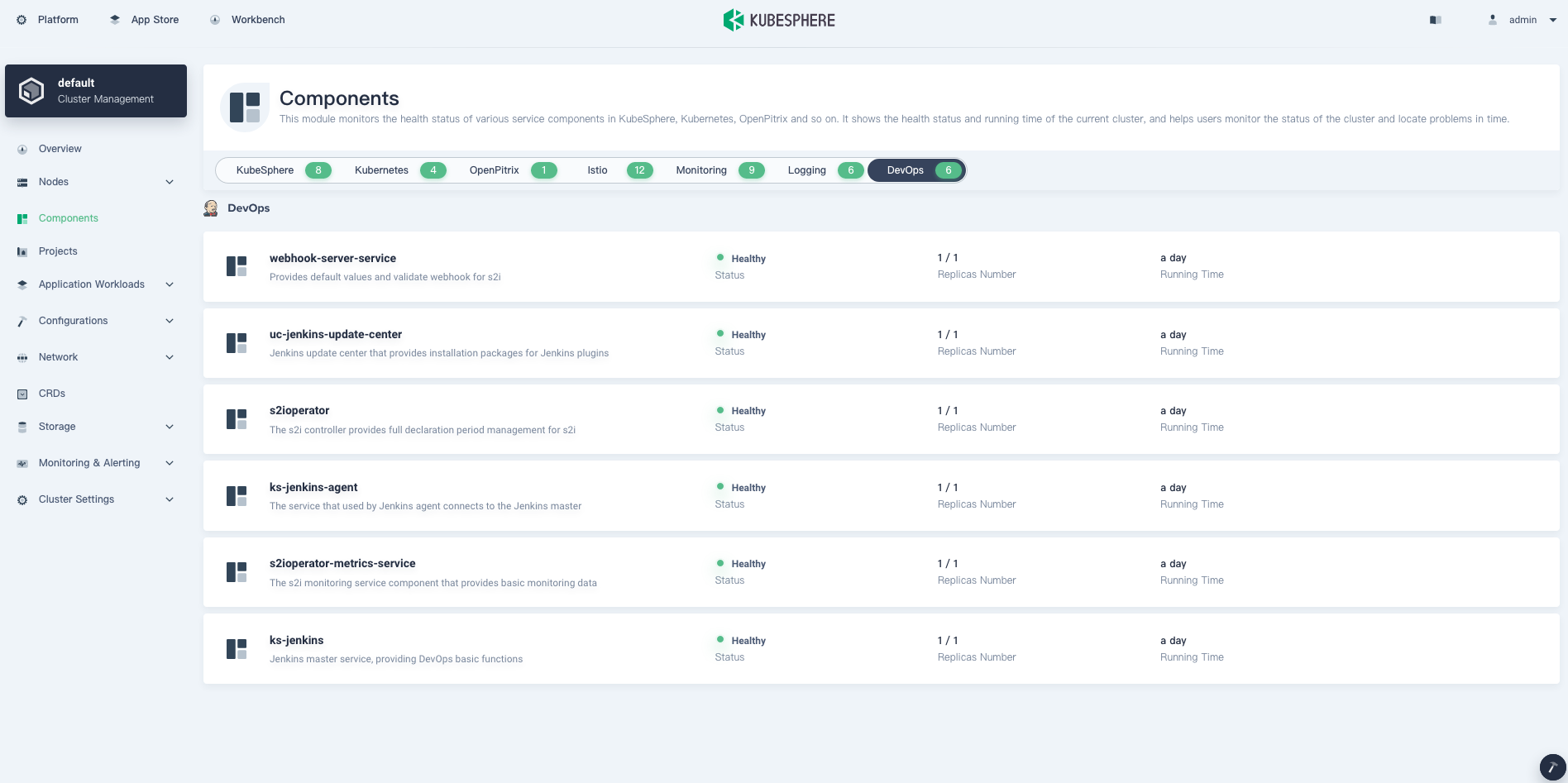
Execute the following command to check the status of Pods:
kubectl get pod -n kubesphere-devops-system
The output may look as follows if the component runs successfully:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ks-jenkins-68b8949bb-jcvkt 1/1 Running 0 1h3m
s2ioperator-0 1/1 Running 1 1h3m
uc-jenkins-update-center-8c898f44f-hqv78 1/1 Running 0 1h14m













 Previous
Previous
