
You are viewing documentation for KubeSphere version:v3.0.0
KubeSphere v3.0.0 documentation is no longer actively maintained. The version you are currently viewing is a static snapshot. For up-to-date documentation, see the latest version.
Pipeline Settings
When you create a pipeline, you can customize its configurations through various settings. This document illustrates these settings in detail.
Prerequisites
- You need to create a workspace, a DevOps project and an account (
project-regular). This account must be invited to the DevOps project with theoperatorrole. For more information, refer to Create Workspaces, Projects, Accounts and Roles. - You need to enable the KubeSphere DevOps System.
Pipeline Settings
Basic Information
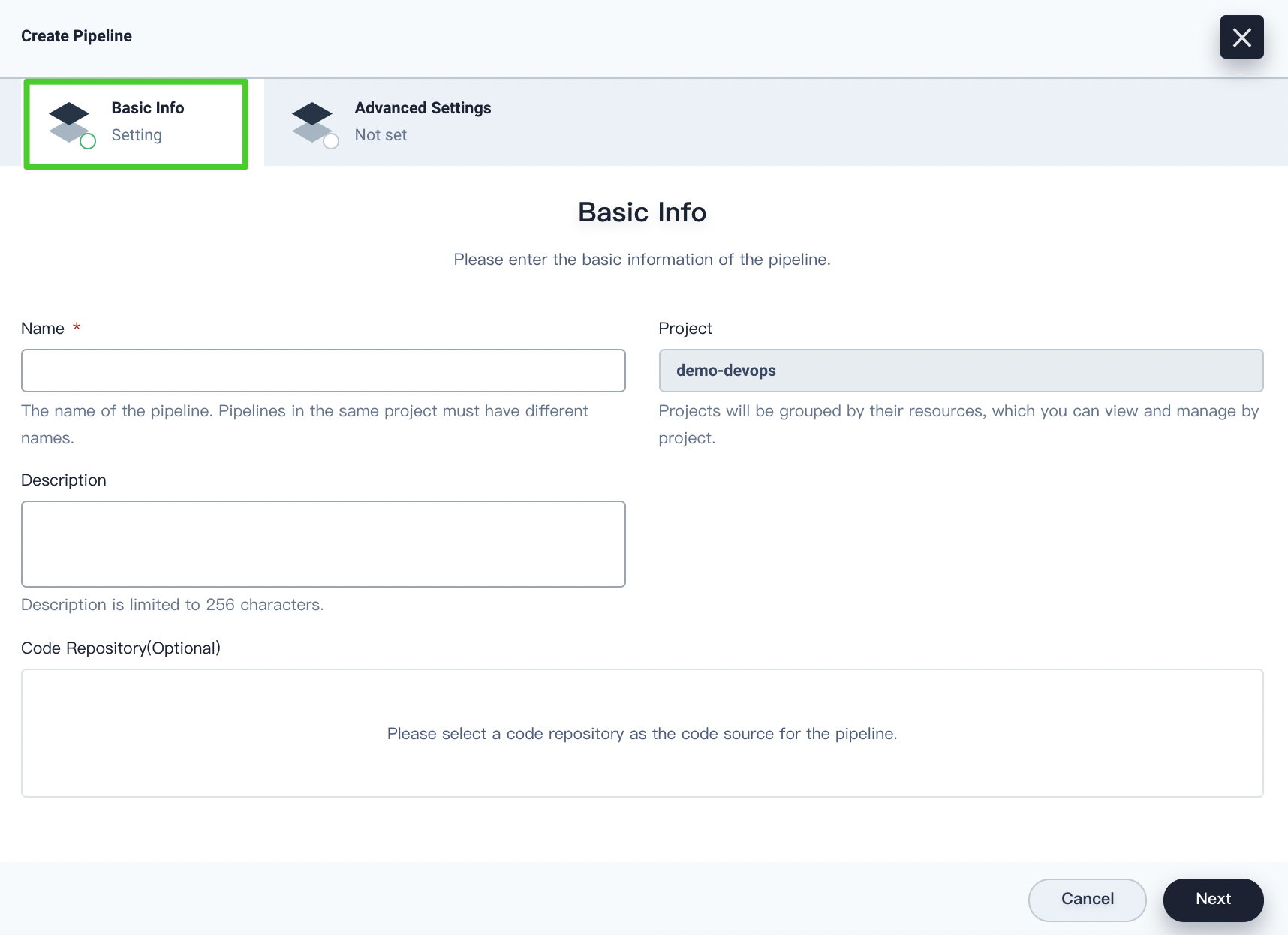
On the Basic Info tab, you can customize the following information:
-
Name. The name of the pipeline. Pipelines in the same DevOps project must have different names.
-
Project. Projects will be grouped by their resources, which you can view and manage by project.
-
Description. The additional information to describe the pipeline. Description is limited to 256 characters.
-
Code Repository (optional). You can select a code repository as the code source for the pipeline. In KubeSphere v3.0, you can select GitHub, Git, SVN, or Bitbucket Server as the code source.
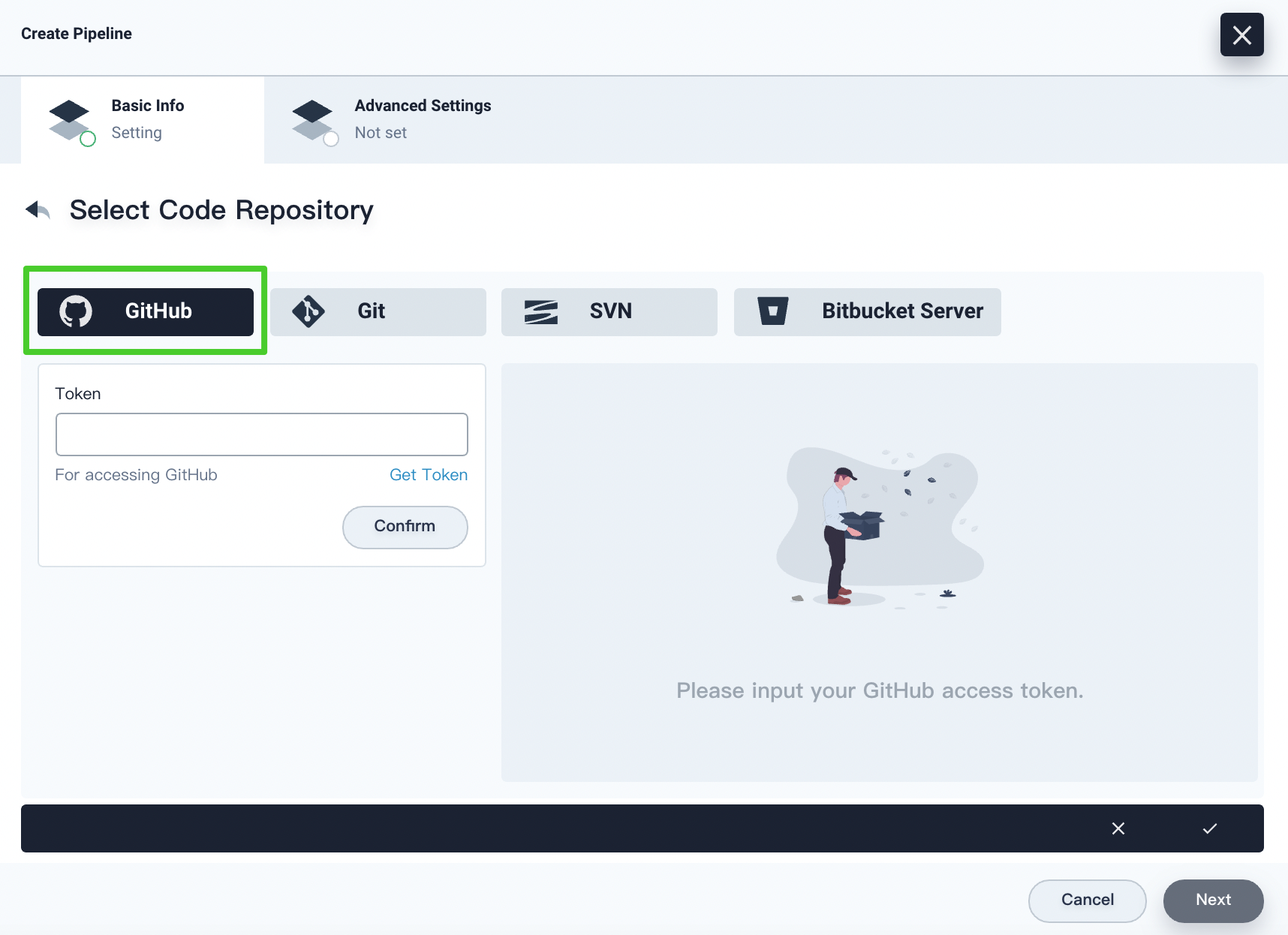
If you select GitHub, you have to specify the token for accessing GitHub. You can click Get Token to generate a new token on GitHub. Click Confirm after entering the token and you can view your repository on the right. Click the √ icon after you finish all operations.
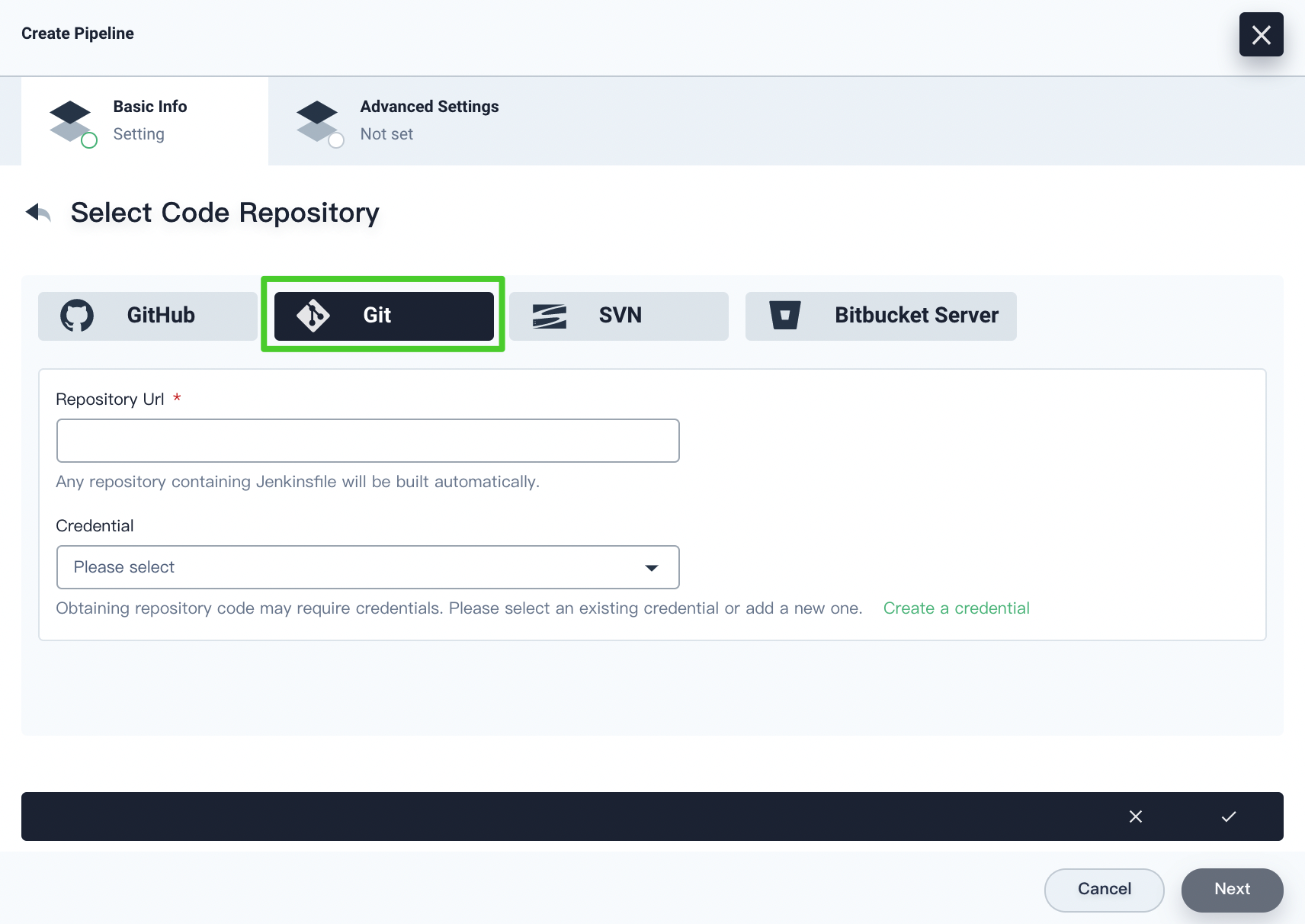
If you select Git, you have to specify the repository URL. You need to specify a credential if it is needed for obtaining repository codes. You can also click Create a credential to create a new credential. Click the √ icon after you finish all operations.
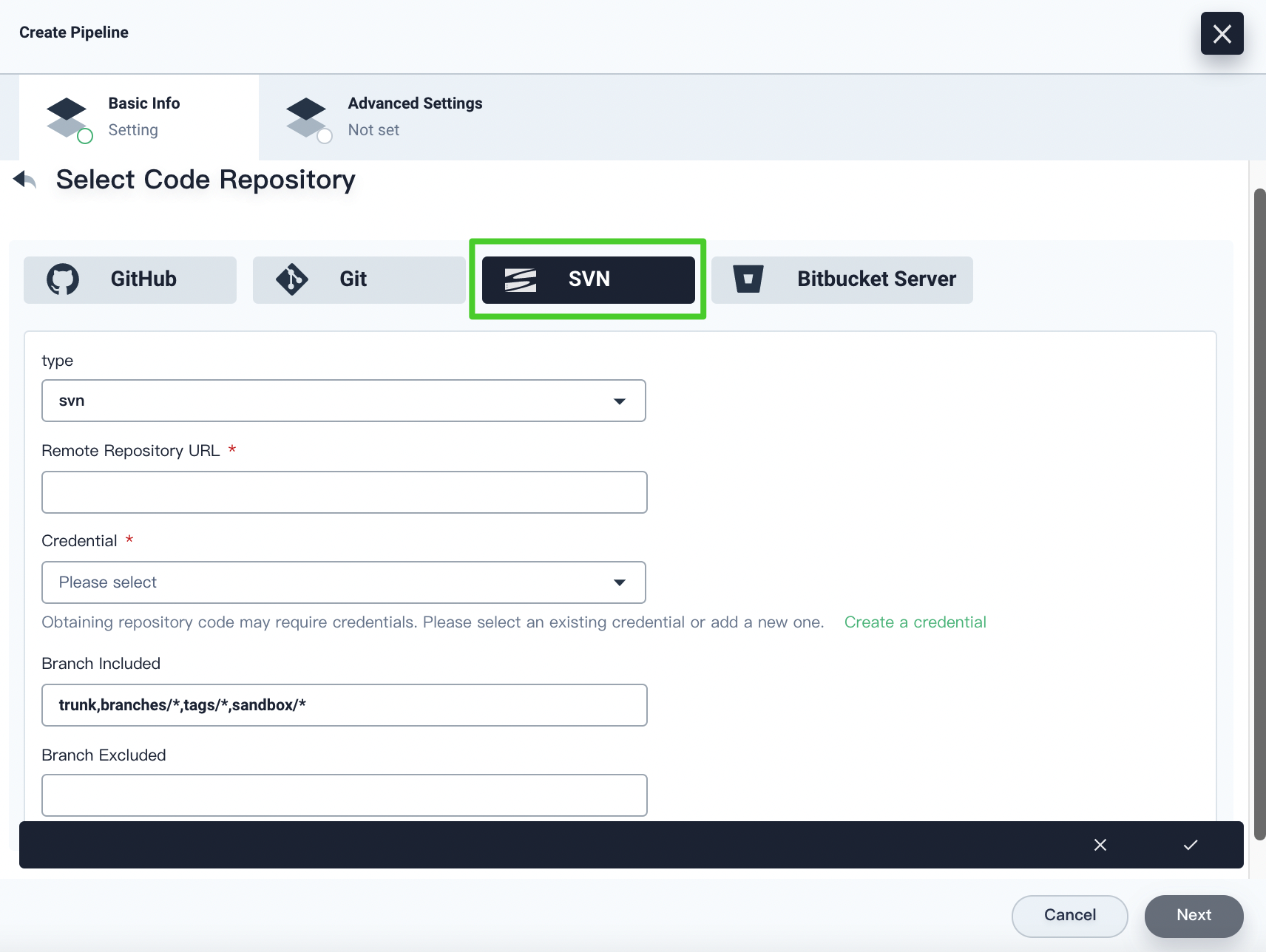
If you select SVN, you have to specify the repository URL and the credential. You can also specify the branch included and excluded based on your needs. Click the √ icon after you finish all operations.
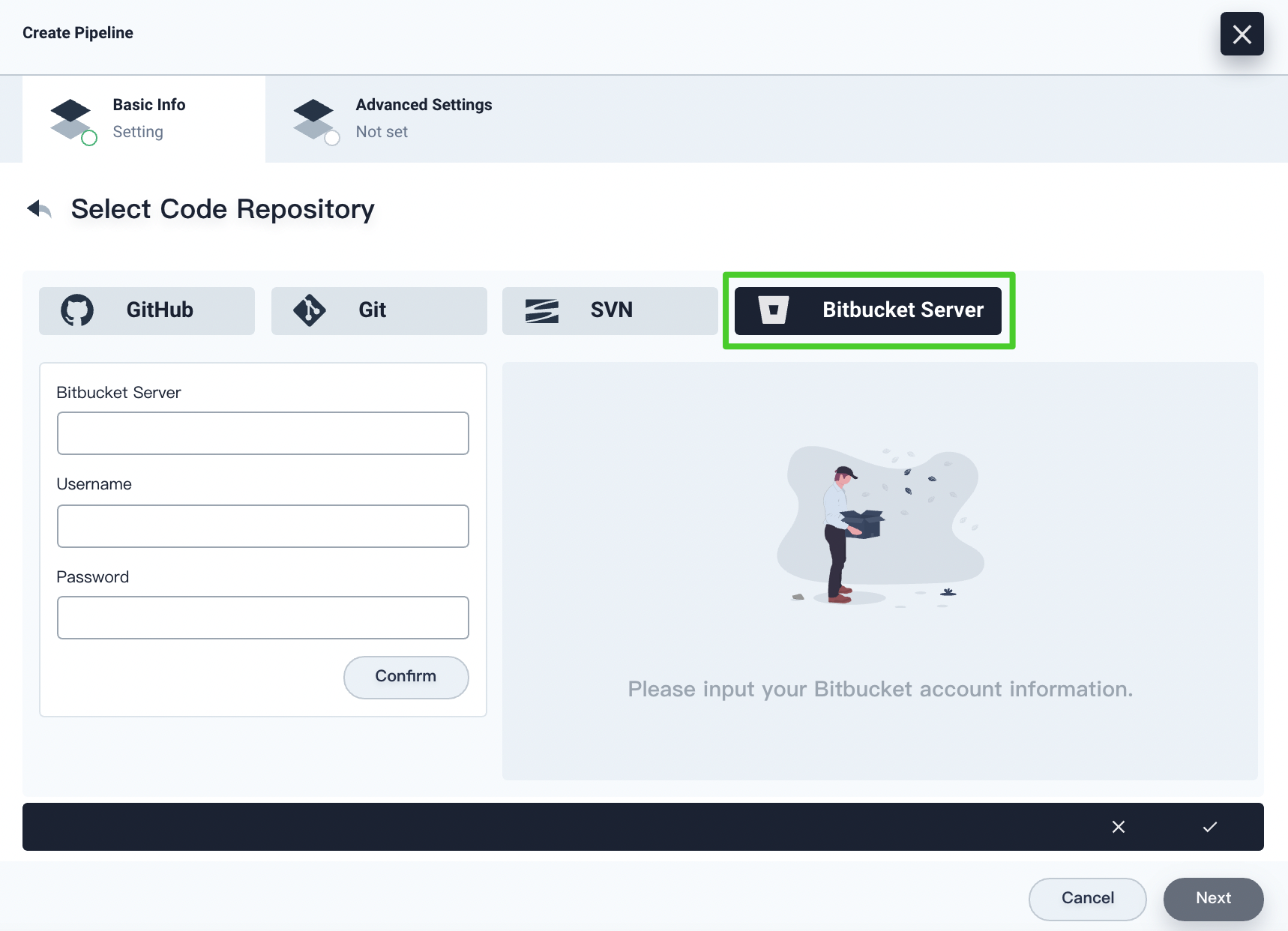
If you select Bitbucket Server, you have to specify the Bitbucket server, username, and password. Click Confirm after entering the information. Click the √ icon after you finish all operations.
Advanced Settings with A Code Repository Selected
If you selected a code repository, you can customize the following configurations on the Advanced Settings tab:
Branch Settings
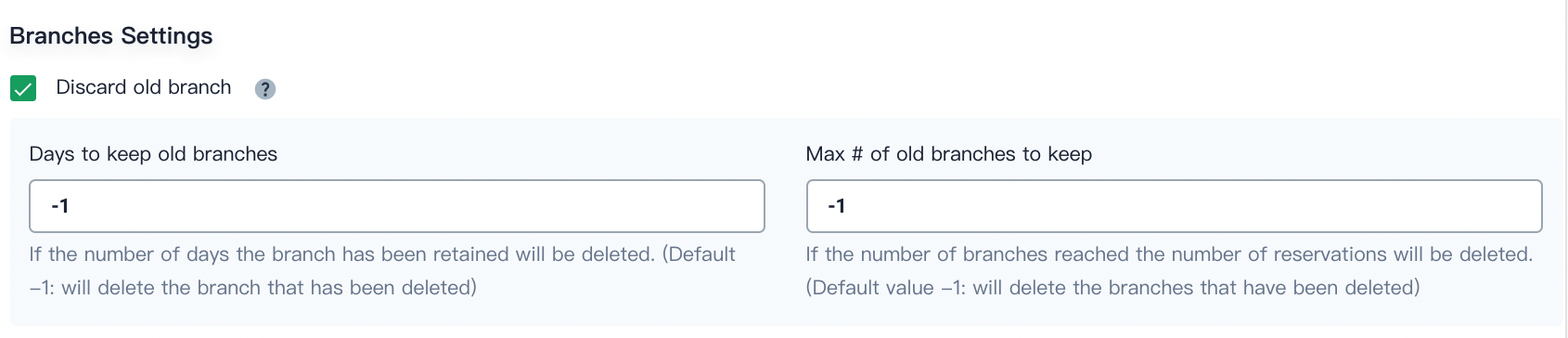
Discard old branch means that the branch record will be discarded all together. The branch record includes console output, archived artifacts and other relevant metadata of specific branches. Fewer branches mean that you can save the disk space that Jenkins is using. KubeSphere provides two options to determine when old branches are discarded:
-
Days to keep old branches. Branches will be discarded after a certain number of days.
-
Maximum number of branches to keep. The oldest branches will be discarded after branches reach a certain amount.
Note
Days to keep old branches and Maximum number of branches to keep apply to branches at the same time. As long as a branch meets the condition of either field, it will be discarded. For example, if you specify 2 as the number of retention days and 3 as the maximum number of branches, any branches that exceed either number will be discarded. KubeSphere prepopulates these two fields with -1 by default, which means deleted branches will be discarded.
Behavioral strategy
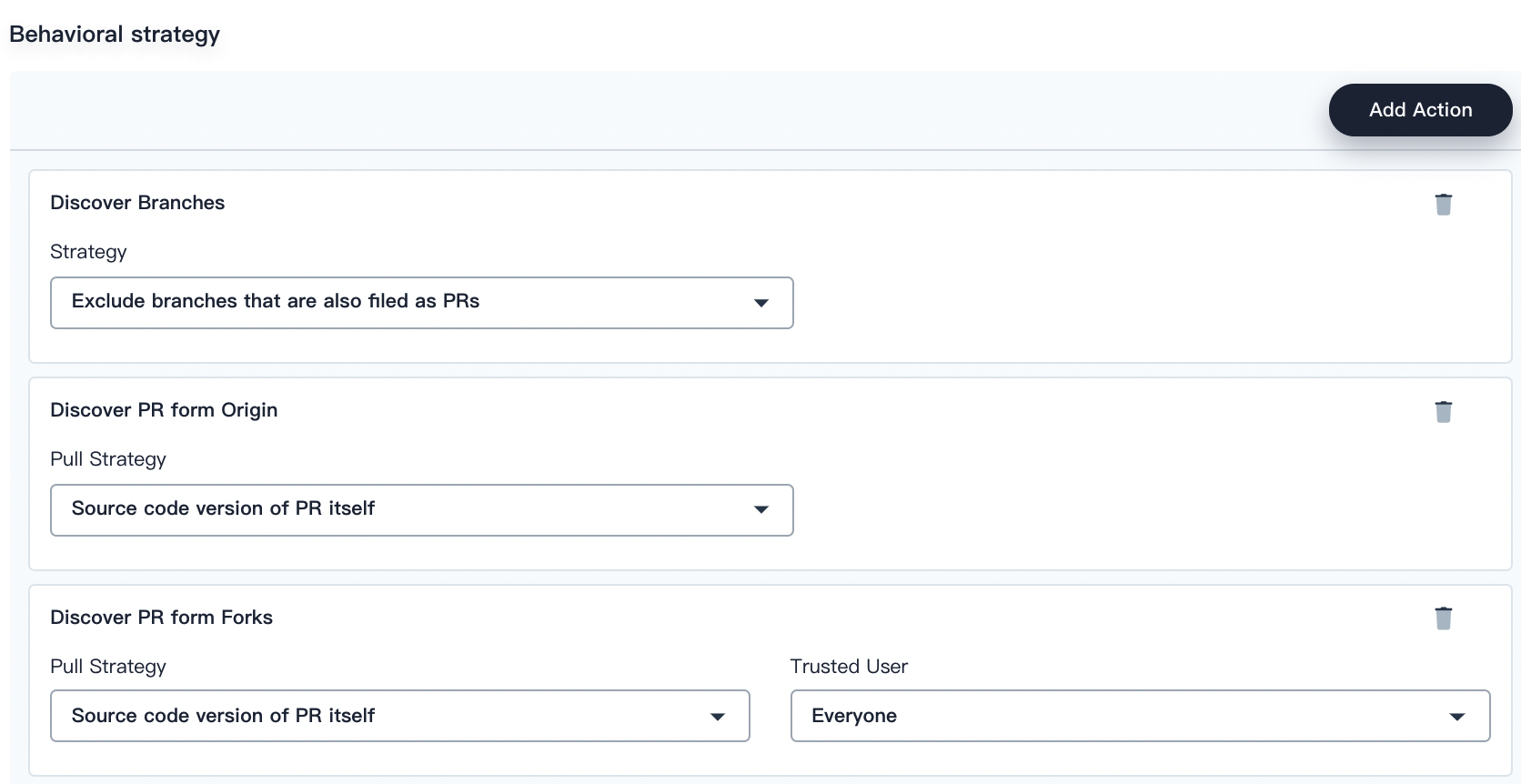
In Behavioral strategy, KubeSphere offers three strategies by default. As a Jenkins pipeline runs, the Pull Request (PR) submitted by developers will also be regarded as a separate branch.
Discover Branches
- Exclude branches that are also filed as PRs. The source branch is not scanned such as the origin’s master branch. These branches need to be merged.
- Only branches that are also filed as PRs. Only scan the PR branch.
- All branches. Pull all the branches from the repository origin.
Discover PR from Origin
- Source code version of PR merged with target branch. A pipeline is created and runs based on the source code after the PR is merged into the target branch.
- Source code version of PR itself. A pipeline is created and runs based on the source code of the PR itself.
- Two pipelines are created when a PR is discovered. KubeSphere creates two pipelines, one based on the source code after the PR is merged into the target branch, and the other based on the source code of the PR itself.
Discover PR from Forks
- Source code version of PR merged with target branch. A pipeline is created and runs based on the source code after the PR is merged into the target branch.
- Source code version of PR itself. A pipeline is created and runs based on the source code of the PR itself.
- Two pipelines are created when a PR is discovered. KubeSphere creates two pipelines, one based on the source code after the PR is merged into the target branch, and the other based on the source code of the PR itself.
- Contributors. The users who make contributions to the PR.
- Everyone. Every user who can access the PR.
- From users with Admin or Write permission. Only from users with Admin or Write permission to the PR.
- Nobody. If you select this option, no PR will be discovered despite the option you select in Pull Strategy.
Script Path

The field of Script Path specifies the Jenkinsfile path in the code repository. It indicates the repository’s root directory. If the file location changes, the script path also needs to be changed.
Scan Repo Trigger
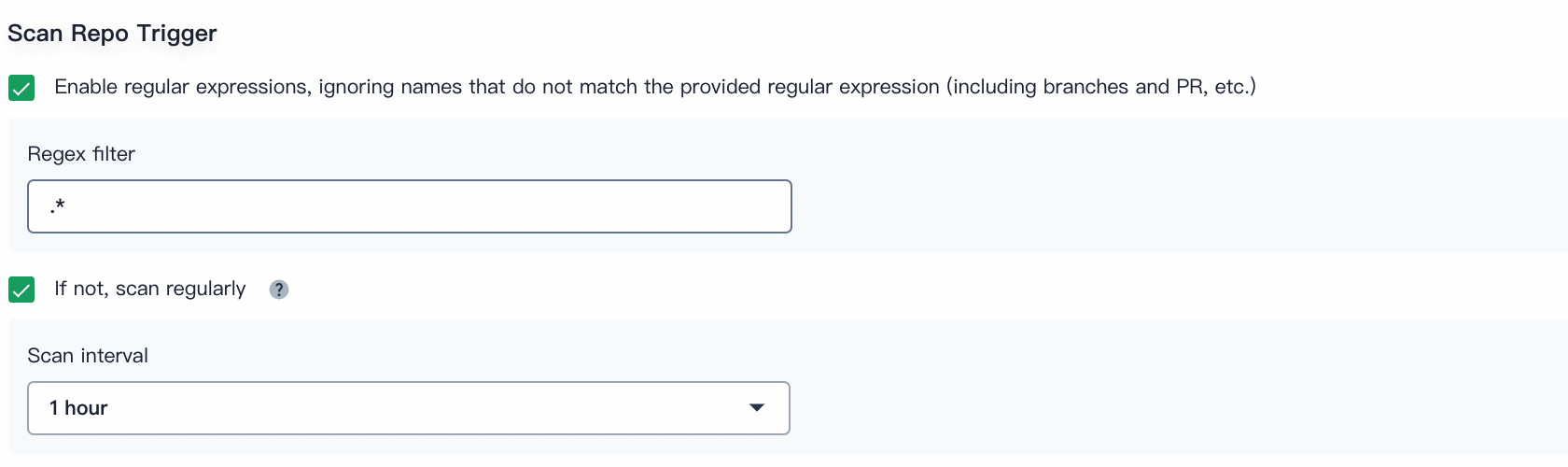
You can check Enable regular expressions, ignoring names that do not match the provided regular expression (including branches and PRs) to specify a regular expression as the trigger for scanning the code repository.
You can also check If not, scan regularly and set the scan interval from the drop-down list.
Build Trigger
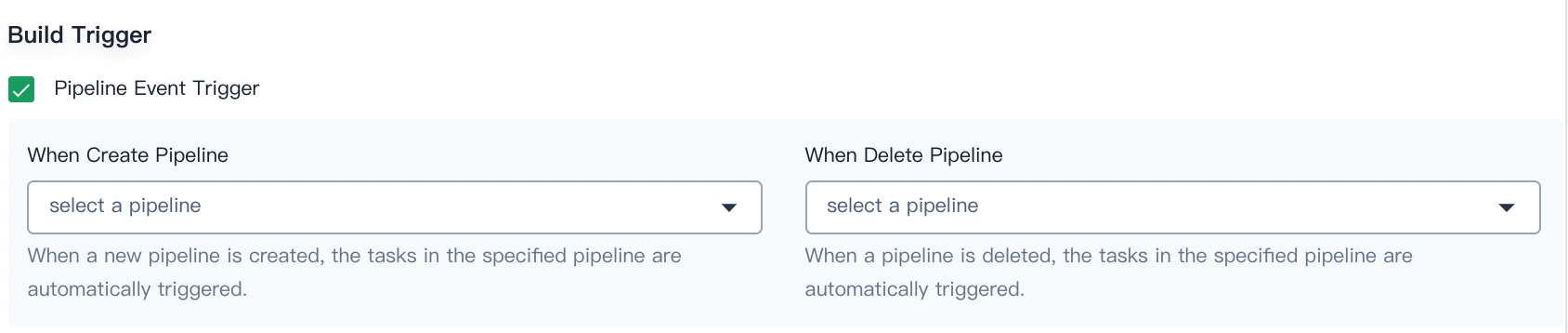
You can select a pipeline from the drop-down list for When Create Pipeline and When Delete Pipeline so that when a new pipeline is created or a pipeline is deleted, the tasks in the specified pipeline can be automatically triggered.
Git Clone Options

- clone depth. The number of commits to fetch when you clone.
- Pipeline clone timeout (in minutes). The number of minutes before which the cloning process has to complete.
- Whether to enable shallow clone. If you enable it, the codes cloned will not contain tags.
Webhook
Webhook is an efficient way to allow pipelines to discover changes in the remote code repository and automatically trigger a new running. Webhook should be the primary method to trigger Jenkins automatic scanning for GitHub and Git (for example, GitLab).
Advanced Settings with No Code Repository Selected
If you don’t select a code repository, you can customize the following configurations on the Advanced Settings tab:
Build Settings
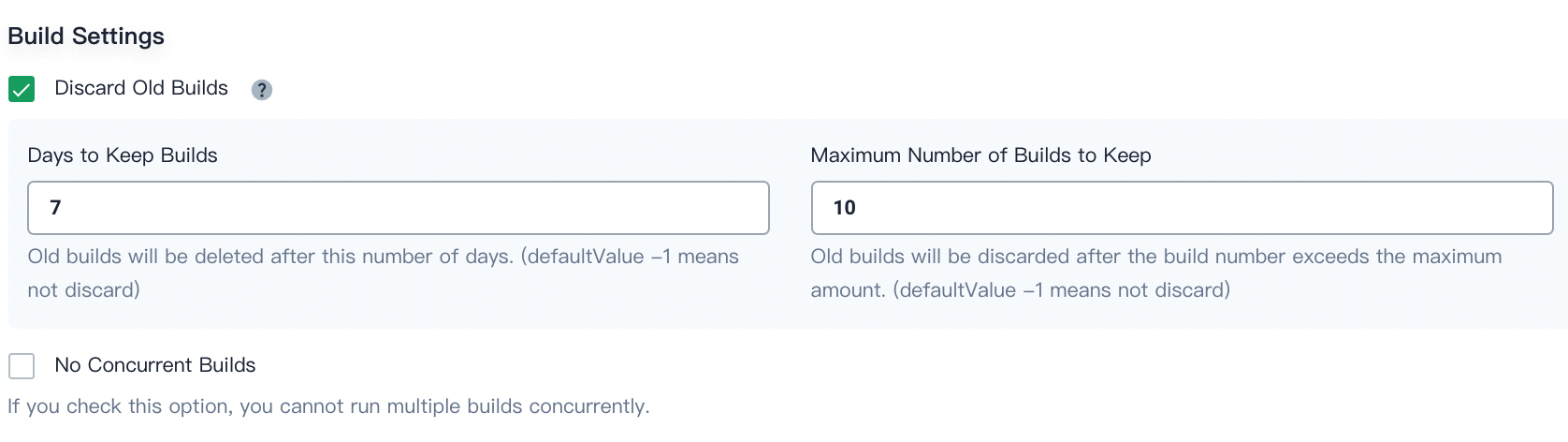
Discard old builds determines when the build records under the branch will be discarded. The build record includes the console output, archived artifacts, and other metadata related to a particular build. Keeping fewer builds saves disk space used by Jenkins. KubeSphere provides two options to determine when old builds are discarded:
-
Days to keep build. The build will be discarded after a certain number of days.
-
Maximum number of builds to keep. If the existing number of builds exceeds the maximum number, the oldest build will be discarded.
Note
These two conditions apply to the build at the same time. If either one is met first, the build will be discarded. -
No concurrent builds. If you check this option, you cannot run multiple builds concurrently.
Parametric Build
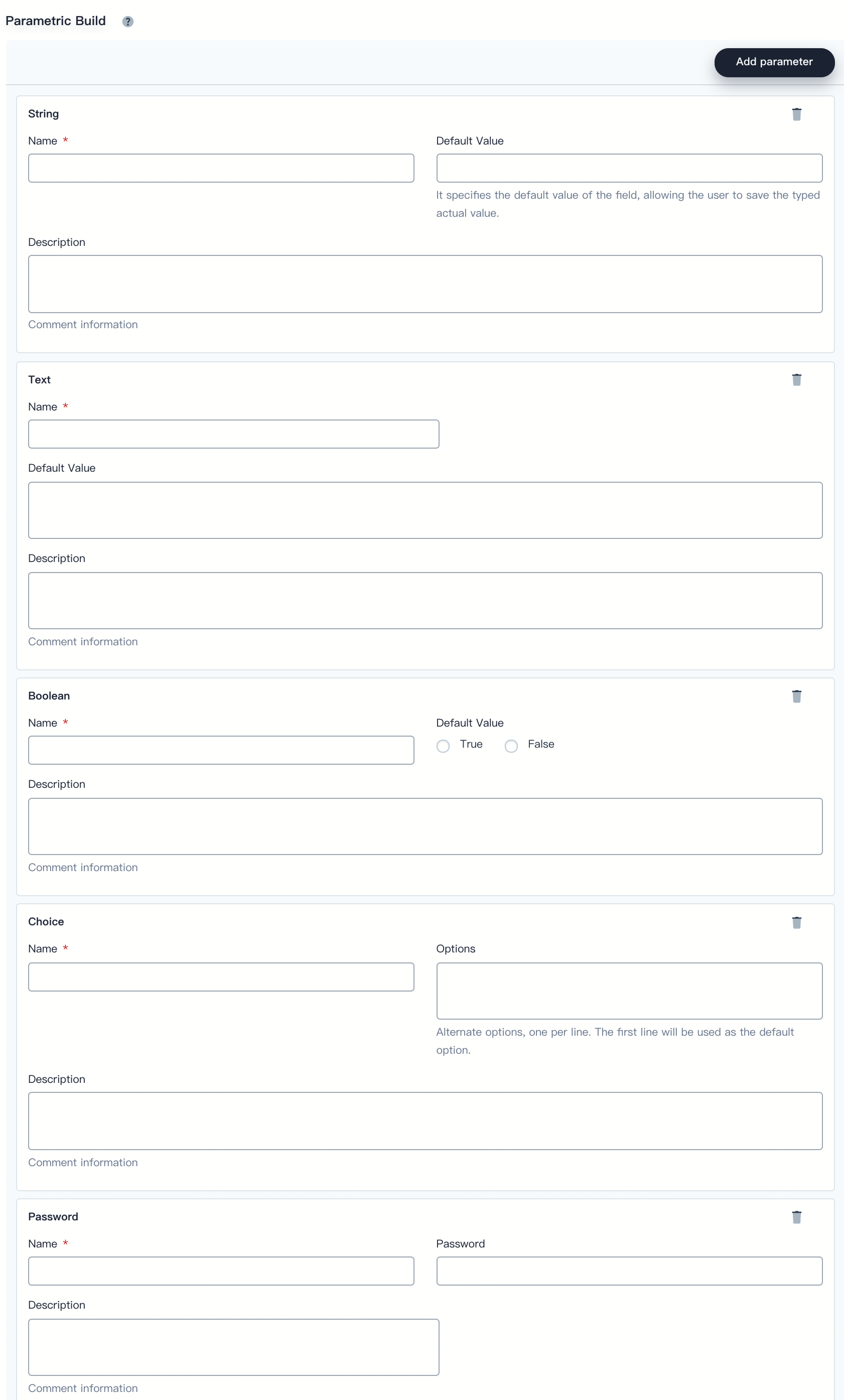
The parameterized build process allows you to pass in one or more parameters when you start to run a pipeline. KubeSphere provides five types of parameters by default, including String, Text, Boolean, Choice, and Password. When you parameterize a project, the build is replaced with a parameterized build, which prompts the user to enter a value for each defined parameter.
Build Trigger
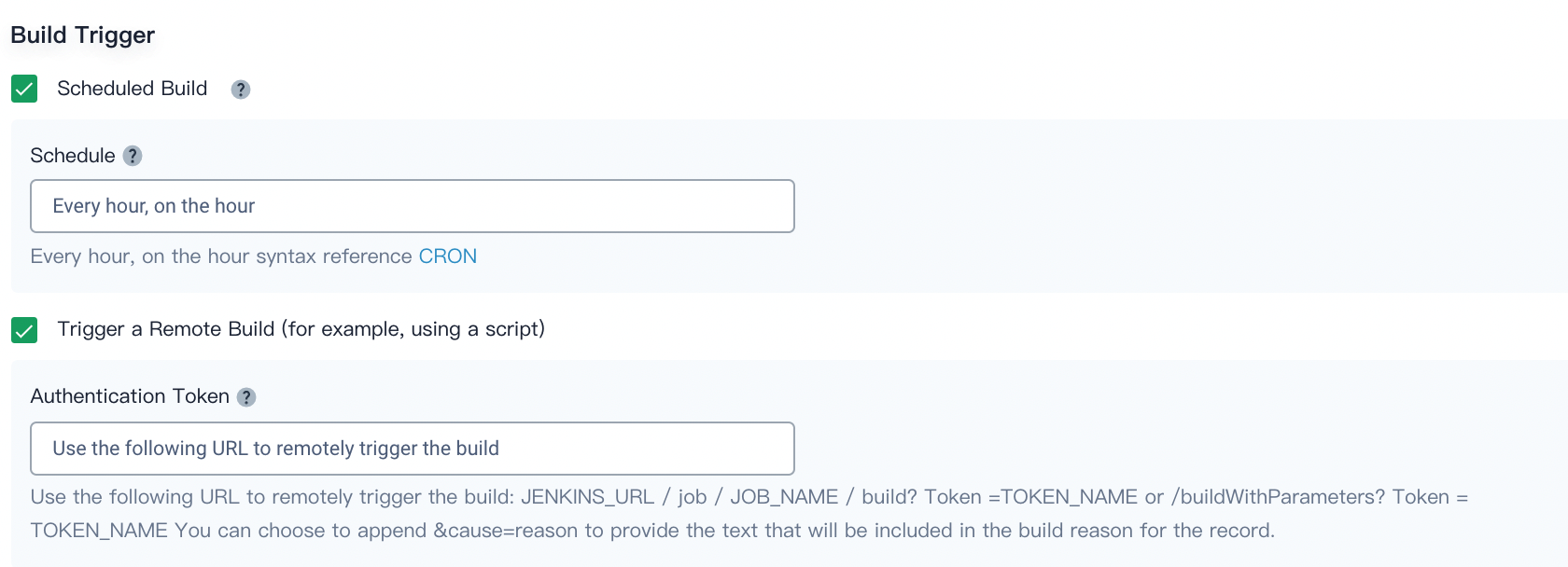
- Scheduled build. It enables builds with a specified schedule. You can click CRON to refer to the detailed cron syntax.
- Trigger a remote build (for example, using a script). If you need to access a predefined URL to remotely trigger the build, you have to check it and provide an authentication token so that only the user who has the token can remotely trigger the build.













 Previous
Previous
